Perlin Power Fractal Noise
[DEPRECATED - Replaced by Power Noise Suite]
Create highly customizable PPF Noise input for ComfyUI generation. Using this novel approach power uses can create generations with high frequency details right in their base generations. In many cases, offers better stabilization then base ComfyUI noise, especially for product conceptualization as seen below:
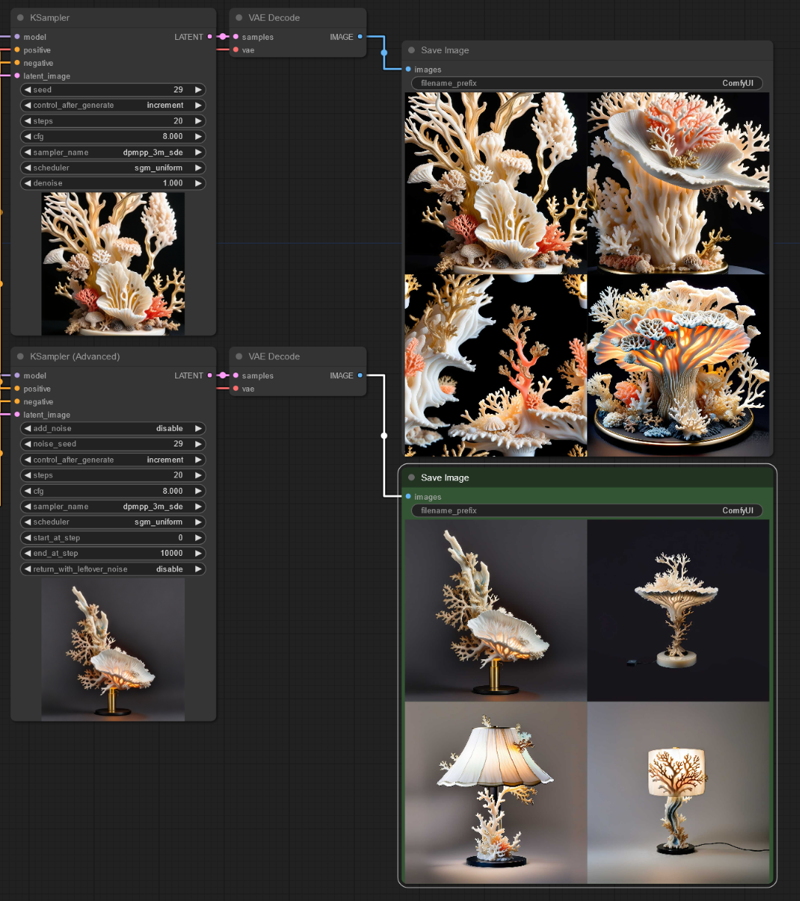
( High frequency noise input allows product generation to be more stable, and centered, following your prompt better )
PPF Noise input seems to help with base generations pixel noise distribution, which in turns helps with post processing techniques such as AI Upscaling, where results show possibly less artifacting:
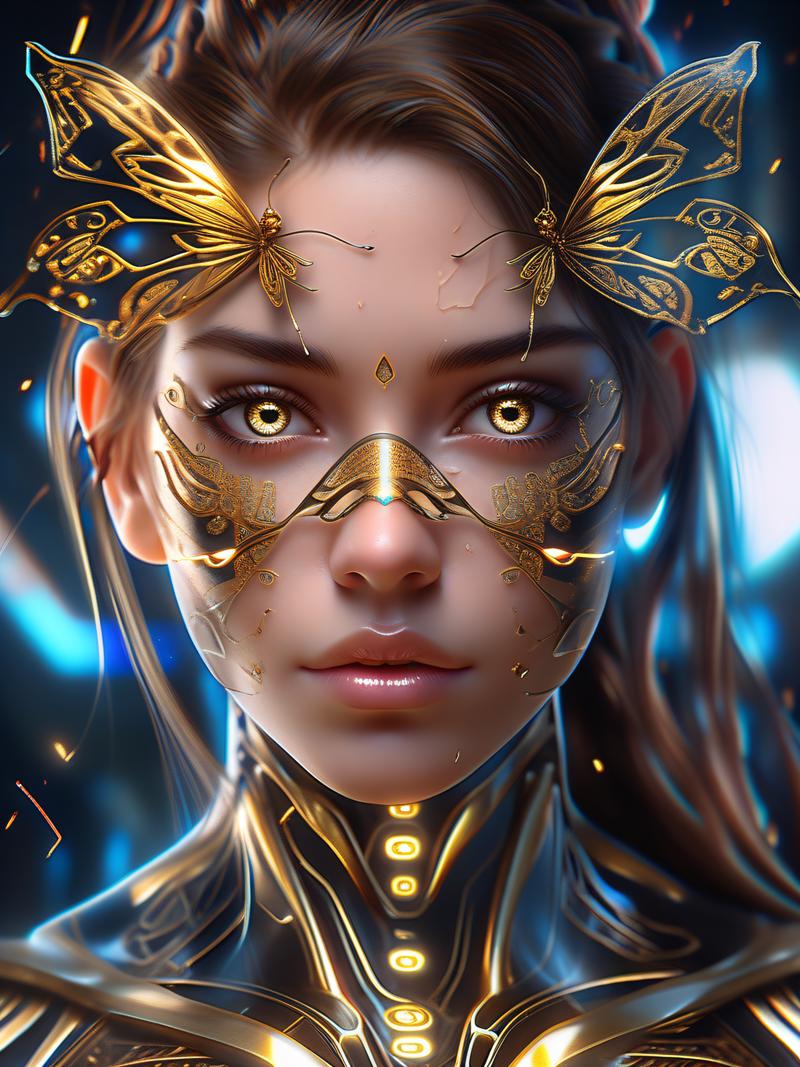

Comptaibility:
PPF Noise seems to be only compatible with certain schedulers/samplers, and to what extent isn't fully understood. Good setups to try is:
dpmpp / kerras
dpmpp / sgm_uniform
Perlin Power Fractal Noisey Latents
Power Fractal Latent Generator
Generate a batch of images with a Perlin power fractal effect.
Installation
Clone the repo to
ComfyUI/custom_nodes. Torch versions do not need requirements.txt installed.If you are using previous non-torch builds, run the requirements.txt against your ComfyUI Python Environment
ComfyUI Standalone Portable example:
C:\ComfyUI_windows_portable\python_embeded\python.exe -s -m pip install -r "C:\ComfyUI_windows_portable\custom_nodes\PPF_Noise_ComfyUI\requirements.txt"
Perlin Power Fractal Noise Parameters
This node generates perlin power fractal noise
Required:
batch_size(int): Number of noisy tensors to generate in the batch.Range: [1, 64]
width(int): Width of each tensor in pixels.Range: [64, 8192]
height(int): Height of each image in pixels.resampling(string): This parameter determines the resampling method used for scaling noise to the latent size. Choose from the following options:"nearest-exact": Nearest-Exact Resampling:
Nearest-neighbor resampling selects the pixel value from the nearest source pixel, resulting in a blocky, pixelated appearance. It preserves the exact values without interpolation.
"bilinear": Bilinear Resampling:
Bilinear interpolation takes a weighted average of the four nearest source pixels, producing smoother transitions between pixels. It's a good choice for general image resizing.
"area": Area Resampling (Antialiasing):
Resampling using pixel area relation, also known as antialiasing, computes pixel values based on the areas of contributing source pixels. It reduces aliasing artifacts and is suitable for preserving fine details.
"bicubic": Bicubic Resampling:
Bicubic interpolation uses a cubic polynomial to compute pixel values based on the 16 nearest source pixels. It provides smoother transitions and better detail preservation, suitable for high-quality resizing.
"bislerp": Bislerp Resampling (Bilinear Sinc Interpolation):
Bislerp interpolation combines bilinear simplicity with sinc function interpolation, resulting in high-quality resizing with reduced artifacts. It offers a balance between quality and computational cost.
X(float): X-coordinate offset for noise sampling.Range: [-99999999, 99999999]
Y(float): Y-coordinate offset for noise sampling.Range: [-99999999, 99999999]
Z(float): Z-coordinate offset for noise sampling.Range: [-99999999, 99999999]
frame(int): The current frame number for time evolution.Range: [0, 99999999]
evolution_factor(float): Factor controlling time evolution. Determines how much the noise evolves over time based on the batch index.Range: [0.0, 1.0]
octaves(int): Number of octaves for fractal generation. Controls the level of detail and complexity in the output.Range: [1, 8]
persistence(float): Persistence parameter for fractal generation. Determines the amplitude decrease of each octave.Range: [0.01, 23.0]
lacunarity(float): Lacunarity parameter for fractal generation. Controls the increase in frequency from one octave to the next.Range: [0.01, 99.0]
exponent(float): Exponent applied to the noise values. Adjusting this parameter controls the overall intensity and contrast of the output.Range: [0.01, 38.0]
scale(float): Scaling factor for frequency of noise. Larger values produce smaller, more detailed patterns, while smaller values create larger patterns.Range: [2, 2048]
brightness(float): Adjusts the overall brightness of the generated noise.-1.0 makes the noise completely black.
0.0 has no effect on brightness.
1.0 makes the noise completely white.
Range: [-1.0, 1.0]
contrast(float): Adjusts the contrast of the generated noise.-1.0 reduces contrast, enhancing the difference between dark and light areas.
0.0 has no effect on contrast.
1.0 increases contrast, enhancing the difference between dark and light areas.
Range: [-1.0, 1.0]
clamp_min(float): The floor range of the noiseRange: [-10.0, 10]
clamp_max(float): The ceiling range of the noiseRange: [-10, 10]
seed(int, optional): Seed for random number generation. If None, uses random seeds for each batch.Range: [0, 0xffffffffffffffff]
device(string): Specify the device to generate noise on, either "cpu" or "cuda".
Optional:
optional_vae(VAE, optional): The optional VAE for encoding the noise.
Returns
tuple(torch.Tensor [latent], torch.Tensor [image])
Cross-Hatch Power Fractal Parameters
This node generates a batch of cross-hatch power fractal noise patterns.
Required:
batch_size(int): Number of noisy tensors to generate in the batch.Range: [1, 64]
width(int): Width of each tensor in pixels.Range: [64, 8192]
height(int): Height of each image in pixels.resampling(string): This parameter determines the resampling method used for scaling noise to the latent size. Choose from the following options:"nearest-exact": Nearest-Exact Resampling:
Nearest-neighbor resampling selects the pixel value from the nearest source pixel, resulting in a blocky, pixelated appearance. It preserves the exact values without interpolation.
"bilinear": Bilinear Resampling:
Bilinear interpolation takes a weighted average of the four nearest source pixels, producing smoother transitions between pixels. It's a good choice for general image resizing.
"area": Area Resampling (Antialiasing):
Resampling using pixel area relation, also known as antialiasing, computes pixel values based on the areas of contributing source pixels. It reduces aliasing artifacts and is suitable for preserving fine details.
"bicubic": Bicubic Resampling:
Bicubic interpolation uses a cubic polynomial to compute pixel values based on the 16 nearest source pixels. It provides smoother transitions and better detail preservation, suitable for high-quality resizing.
"bislerp": Bislerp Resampling (Bilinear Sinc Interpolation):
Bislerp interpolation combines bilinear simplicity with sinc function interpolation, resulting in high-quality resizing with reduced artifacts. It offers a balance between quality and computational cost.
frequency(float): Frequency parameter for fractal generation. Determines the frequency of the cross-hatch pattern.Range: [0.001, 1024.0]
octaves(int): Number of octaves for fractal generation. Controls the level of detail and complexity in the output.Range: [1, 32]
persistence(float): Persistence parameter for fractal generation. Determines the amplitude decrease of each octave.Range: [0.001, 2.0]
color_tolerance(float): Tolerance parameter for color mapping. Affects the variety of colors in the output.Range: [0.001, 1.0]
num_colors(int): Number of colors to use in the output.Range: [2, 256]
angle_degrees(float): Angle in degrees for the cross-hatch pattern.Range: [0.0, 360.0]
brightness(float): Adjusts the overall brightness of the generated noise.-1.0 makes the noise completely black.
0.0 has no effect on brightness.
1.0 makes the noise completely white.
Range: [-1.0, 1.0]
contrast(float): Adjusts the contrast of the generated noise.-1.0 reduces contrast, enhancing the difference between dark and light areas.
0.0 has no effect on contrast.
1.0 increases contrast, enhancing the difference between dark and light areas.
Range: [-1.0, 1.0]
blur(float): Blur parameter for the generated noise.Range: [0.0, 1024.0]
clamp_min(float): The floor range of the noise.Range: [-10.0, 10.0]
clamp_max(float): The ceiling range of the noise.Range: [-10.0, 10.0]
seed(int, optional): Seed for random number generation. If None, uses random seeds for each batch.Range: [0, 0xffffffffffffffff]
device(string): Specify the device to generate noise on, either "cpu" or "cuda".
Optional:
optional_vae(VAE, optional): The optional VAE for encoding the noise.
Returns
tuple(LATENT, IMAGE): A tuple containing the generated latent tensor and image tensor.
Blend Latents Parameters
This node provides a method for blending two latent tensors.
Required:
latent_a(LATENT, required): The first input latent tensor to be blended.latent_b(LATENT, required): The second input latent tensor to be blended.operation(string, required): The blending operation to apply. Choose from the following options:add: Combines two images by adding their pixel values together.
bislerp: Interpolates between two images smoothly using the factor
t.color dodge: Brightens the base image based on the blend image. It creates a high-contrast effect by making bright areas of the blend image affect the base image more.
cosine interp: Interpolates between two images using a cosine function.
cuberp: Blends two images by applying a cubic interpolation.
difference: Subtracts one image from another and takes the absolute value. It highlights the differences between the two images.
exclusion: Combines two images using an exclusion formula, resulting in a unique contrast effect.
glow: Create a glow effect based on the blend image. Similar to pin light, but darker.
hard light: Combines two images in a way that enhances the contrast. It creates a sharp transition between light and dark areas.
lerp: Linearly interpolates between two images based on the factor. It creates a simple linear transition.
linear dodge: Brightens the base image by adding the blend image, creating a high-key effect.
linear light: Blends two images to enhance contrast. It brightens or darkens the base image based on the blend image.
multiply: Multiplies the pixel values of two images, resulting in a darker image with increased contrast.
overlay: Combines two images using an overlay formula. It enhances the contrast and creates a dramatic effect.
pin light: Combines two images in a way that preserves the details and intensifies the colors.
random: Adds random noise to both images, creating a noisy and textured effect.
reflect: Combines two images in a reflection formula. A interesting blend to say the least.
screen: Brightens the base image based on the blend image, resulting in a high-key effect.
slerp: Spherically interpolates between two images, creating a smooth and curved transition.
subtract: Subtracts the blend image from the base image, resulting in a darker image.
vivid light: Enhances the vividness of colors in the base image based on the blend image. It intensifies the colors.
blend_ratio(FLOAT, required): The blend ratio betweenlatent_aandlatent_b.Default: 0.5
Range: [0.01, 1.0]
blend_strength(FLOAT, required): The strength of the blending operation.Default: 1.0
Range: [0.0, 100.0]
Optional:
mask(MASK, optional): An optional mask tensor to control the blending region.set_noise_mask(string, optional): Whether to set the noise mask. Choose from "false" or "true".normalize(string, optional): Whether to normalize the resulting latent tensor. Choose from "false" or "true".clamp_min(FLOAT, optional): The minimum clamping range for the output.Default: 0.0
Range: [-10.0, 10.0]
clamp_max(FLOAT, optional): The maximum clamping range for the output.Default: 1.0
Range: [-10.0, 10.0]
Returns
tuple(LATENT,): A tuple containing the blended latent tensor.
Images as Latents Parameters
This node converts IMAGE to LATENT format, without encoding them. Really only useful for raw noise.
Required:
images(IMAGE): Input images to be converted into latent tensors.resampling(string): This parameter determines the resampling method used for scaling images to the latent size. Choose from the following options:"nearest-exact": Nearest-Exact Resampling:
Nearest-neighbor resampling selects the pixel value from the nearest source pixel, resulting in a blocky, pixelated appearance. It preserves the exact values without interpolation.
"bilinear": Bilinear Resampling:
Bilinear interpolation takes a weighted average of the four nearest source pixels, producing smoother transitions between pixels. It's a good choice for general image resizing.
"area": Area Resampling (Antialiasing):
Resampling using pixel area relation, also known as antialiasing, computes pixel values based on the areas of contributing source pixels. It reduces aliasing artifacts and is suitable for preserving fine details.
"bicubic": Bicubic Resampling:
Bicubic interpolation uses a cubic polynomial to compute pixel values based on the 16 nearest source pixels. It provides smoother transitions and better detail preservation, suitable for high-quality resizing.
"bislerp": Bislerp Resampling (Bilinear Sinc Interpolation):
Bislerp interpolation combines bilinear simplicity with sinc function interpolation, resulting in high-quality resizing with reduced artifacts. It offers a balance between quality and computational cost.
Returns
tuple(LATENT, IMAGE): A tuple containing the generated latent tensor and the input images.



